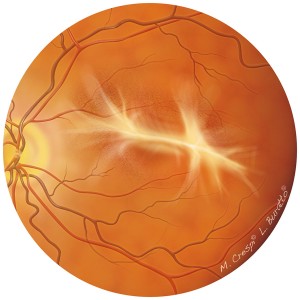
Macular pucker
Macular Pucker is a relatively common maculopathy that affects adults.
It is caused by a small, thin membrane that forms on the surface of the retina, in the region of the macula, and for this reason it is also called the ‘epiretinal membrane’. This transparent membrane looks like the plastic film used in the kitchen to cover food.
Once it has been formed, this membrane may shrink and this contraction will deform the retina below as though it was scrunched (puckered). The contraction of the epiretinal membrane is a slow process, it never occurs unexpectedly. Only during this process of macular deformation will the patient begin to perceive the various symptoms.
Normally a patient affected by macular pucker will complain of distorted vision, and will be affected by metamorphopsia. The distortion the patient reports will be proportional to the degree of deformation of the retina: the lower the degree of distortion, the lower and less invalidating the symptoms perceived.
Not all macular puckers evolve sufficiently to provoke important deformations in the patient’s sight. The epiretinal membrane will be stable for a considerable period of time, sometimes even years.
Diagnosis of macular pucker
Macular pucker can be diagnosed with a careful specialist visit to the eye doctor. An OCT is extremely important for the diagnosis and the evaluation of macular pucker. The results of the OCT can determine the degree of retinal deformation provoked by the membrane and particularly the degree of retinal deformation caused by the membrane; and in particular, it allows the specialist to control the condition over time to determine whether the contraction of the epiretinal membrane has increased or has remained stable.
Treatment of macular pucker
The treatment for macular pucker is surgical. In order to reduce the deformation of the retina, it is necessary to remove the epiretinal membrane created. A vitrectomy of the epiretinal membrane associated with peeling (detachment and removal of the membrane) is the treatment indicated in the cases of macular pucker that have caused an important reduction in the patient’s sight.